
. Improvements in tread performance, rolling resistance reduction, handling, and durability have been well documented. As vehicles have evolved over the past 20 years, tyres have had to adjust along with them. Larger vehicles, higher performing vehicles, and light-weighting, along with the introduction of electric vehicle technology, are all trends that have steered development over the years.
 Through all of it, several key areas in tyre testing have remained steady. Tyres need to meet minimum safety and performance standards as dictated by governments and vehicle OEMs.
Through all of it, several key areas in tyre testing have remained steady. Tyres need to meet minimum safety and performance standards as dictated by governments and vehicle OEMs.
• Tyre durability testing depends on a variety of industry test standards such as endurance testing on a drum.
• Wet stopping distance, tread wear, and winter traction testing have very specific on-vehicle testing requirements.
• Rolling resistance testing utilises a couple standardised test methods to measure the amount of hysteretic energy loss from a rolling tyre on a drum and specified surface.
• Force and moment testing on a moving belt has been used to characterise tyre performance for vehicle design as it relates to cornering and other use conditions.
As time has passed, tyres have been asked to do more and more on vehicles. While the testing methodology has remained similar, conditions have been altered to accommodate these vehicle performance expectations. And while reducing testing time has always been a goal, many of these standard tests still require the same amount of time to conduct.
Because much of tyre testing has been standardised over the years, many facets of the industry can use tyre testing data as a unifying benchmark for evaluating specific performance criteria. For OEMs, the data is valuable to the vehicle development process. For tyre companies, the data is used in a marketing context to compare and contrast features for consumers. Trucking fleets use the data to optimise their operations and reduce costs and fuel consumption. Consistency in testing methodology provides the industry with a unifying foundation of benchmarking data.
That being said, older methods are always being reviewed for obsolescence. For example, NHTSA in the United States is currently considering the removal of test standards for bead unseat and plunger energy testing that were originally developed for bias ply tyre designs.
There are always efforts to look at novel ways of improving the tyre testing process and increasing speed to market. For example, experimenting with different surfaces for drum and belt testing of tyres continues to take place in an attempt to more closely replicate an infinite number of real-life surface conditions. Man-made snow has been developed to extend testing seasons and try to mirror natural snow in an indoor environment. As the industry learns more about how pressure loss impacts rolling resistance and fuel efficiency, more methods have been developed to measure how well different inner liner materials maintain steady tyre pressure. Tyre companies can more readily choose the right materials of construction to suit performance requirements by using material property data from finite element analysis.
Many of these testing methodologies are trending towards virtual testing and modelling of tyre performance. And while tyre modelling has been around since the 1980s, the amount of data and range of data measurement required has increased exponentially.
The key automotive trends driving tyre development going forward continue to be electrification and autonomy. These trends will bring their own challenges to testing and validation. Electrification will present some traditional challenges with new applications, such as managing heavier loads, more aggressive torque / tread wear, reducing noise, and lowering rolling resistance. New materials and constructions are being developed to accommodate these unique challenges for electric vehicles. Tyre tuning will become exceptionally important as second-life tyres are brought into the mix, as consumers will want consistent performance.
From the perspective of autonomous vehicles, sensors and tyre intelligence are being added to provide new data sources for autonomous systems. Tyres equipped with these sensors will have to undergo the same endurance, durability, and performance tests to ensure the sensor can function as designed when faced with the same rigors as the tyre. Depending on where the sensors are mounted in the tyre/wheel assembly, normal tyre dynamics could adversely affect the accuracy of measurements or transmission of data to the vehicle. As aftermarket tires and sensors are developed, testing and validation should follow the same standards to simplify service and compatibility for consumers. Ease of replacement will be critical, as this directly affects the consumer and dealers.
There will continue to be developments and ongoing efforts to improve the fidelity and range of tyre testing data. These improvements will strive to speed up development cycles and improve virtual models going forward. However, the established standards and protocols continue to provide a steadfast and reliable set of tools that development teams, independent evaluators, and testing organisations can use to address new challenges and ensure that the ultimate goal of safety is met for regulatory bodies and consumers.
Dr. James A. Popio is Vice President of Operations - North America of the Smithers Materials Science and Engineering division. Prior to his current role, he was Vice President and General Manager of Smithers in the United Kingdom. Before that, he was General Manager and Director of Engineering at Smithers' Tire and Wheel Testing Laboratory in Ravenna, Ohio.
Jim has worked with the tyre and rubber industry for 20 years and has spent his professional career working for and/or with tyre companies, tyre dealers, automotive OEMs, industry suppliers, manufacturers, standards organisations and government agencies.
Jim has extensive experience in tyre performance, characterisation, and methods development. His specialty areas of expertise are force and moment, endurance, aging, compliance, indoor wear, rolling resistance, and characterisation for modelling. Jim is a regular contributor to industry journals as well as a chair and speaker at major tyre and rubber conferences. Jim has a PhD in engineering and MS, and BS in mechanical engineering from the University of Akron
Bridgestone To Intro Fleet Portal With Automation And AI Capabilities At TMC 2026
- By TT News
- March 12, 2026

Bridgestone Americas is set to introduce its new Fleet Portal platform at the upcoming Technology and Maintenance Council (TMC) Annual Meeting and Transportation Technology Exhibition, taking place from 16 to 19 March 2026 in Nashville. Designed to streamline and simplify fleet management, the platform consolidates essential digital tools into a single, unified interface to help commercial fleets enhance operational efficiency.
The web-based Fleet Portal brings together various fleet management systems, allowing users to access multiple services with just one login. Key features include oversight of accounts, user permissions, vehicle assets and service records, as well as billing, performance reporting and support resources. The portal also provides direct links to other Bridgestone applications. Integrated within the platform is the Service Dispatch solution, which connects fleets with the Bridgestone Commercial Dealer Network, automates technician deployment and enables comprehensive tracking of service documentation and digital data.
To boost productivity, the platform incorporates automation to analyse data, recommend actions and improve search functionality. Initial features include an automated workflow for service events that reduces duplicate data entry and accelerates tyre repairs based on fleet profiles. A streamlined search function allows quick access to technical documents, troubleshooting guides and reports, while centralised network access provides instant connections to dealer locations and training materials, cutting down on resolution time.
Future enhancements for the Fleet Portal will include AI-powered analytics and advanced workflow automation, aligning with Bridgestone’s broader strategy to integrate artificial intelligence across its customer support tools. At the event, Bridgestone’s booth (#2513) will also feature its latest truck and retread tyres tailored for various applications, with representatives available throughout the exhibition hours.
Josh Holland, Vice President – Network and Fleet Care Solutions, Bridgestone Americas, said, “With the new Fleet Portal, we can centralise all tools and data into a single digital experience for fleets. This integration is key to Bridgestone's customer strategy to connect our fleet solutions in ways that deliver stronger performance with less complexity.”
Steve Hoeft, President – Commercial Truck Group, Bridgestone Americas, said, “Centralising insights and workflows means less manual work, faster decisions and full operational visibility. It’s a major step in the industry’s digital evolution, enabling fleets to move from reactive problem-solving to proactive decision-making and management."
TROESTER Expands Automation Portfolio With TROESTER Robotics
- By TT News
- March 10, 2026

TROESTER GmbH & Co. KG expanded its automation capabilities in 2025 by acquiring SC OTOMASYON, a Turkish company based in Istanbul. The acquired business now operates as TROESTER Robotics and has been fully integrated into the TROESTER Group structure. This strategic move enhances the company’s expertise in automation and robotics while creating synergies that support future growth.
The acquisition marks an important step in TROESTER’s long-term strategy of developing autonomous production systems that enable fully integrated, low-labour manufacturing processes. Through TROESTER Robotics, the company now gains access to robotic applications across the entire tyre factory, from individual process stations to fully networked production lines. This capability addresses growing global demand for robotic solutions, as manufacturers in Europe, China and North America increasingly face workforce shortages.
With this integration, TROESTER can now meet that demand with comprehensive solutions from a single source. Both teams look forward to working together and jointly advancing technologically leading automation solutions.
Thomas Holzer, CEO, TROESTER GmbH & Co. KG, “The company brings start-up spirit, agility and strong innovative capabilities, while TROESTER contributes decades of experience, established commercial structures, a global sales network and longstanding customer relationships. Together, this creates a clear competitive advantage and a USP that sets us apart in the market.”
- Dunlop
- Sumitomo Rubber Industries
- SENSING CORE Technology
- Tyre Load Detection
- Tyre Air Pressure Detection
- Ruichi
- Ruichi C5
SENSING CORE Technology Debuts In China’s Commercial EVs With Tyre Load Detection Feature
- By TT News
- March 04, 2026
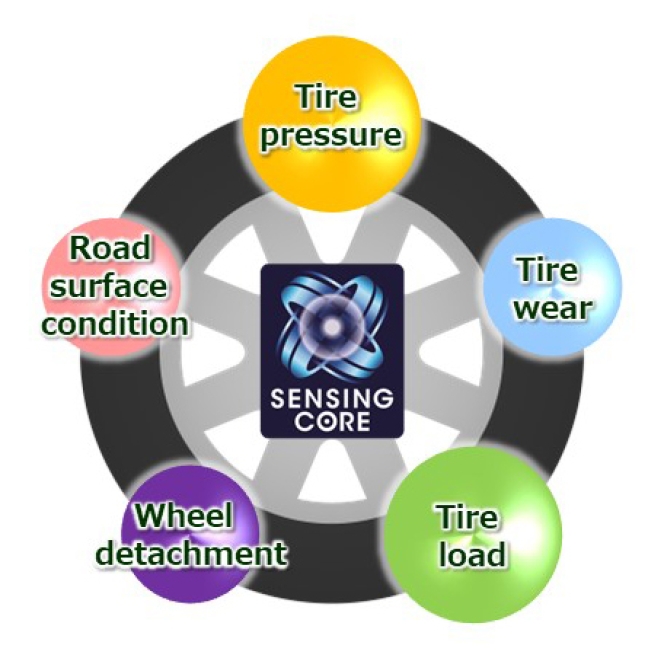
Dunlop (company name: Sumitomo Rubber Industries, Ltd.) has secured the first commercial deployment of its SENSING CORE technology in China. The system's ‘tyre load detection’ and ‘tyre air pressure detection’ functions have been adopted by Chongqing Ruichi Automotive Industry Co., Ltd. (Ruichi) for its new electric commercial vehicle model, the Ruichi C5. This marks both the technology's entry into the Chinese market and the global debut of Dunlop's tyre load detection capability.
The load detection function monitors changes in cargo weight and distribution in real time, feeding data to the vehicle's control system. This reduces driving instability during starting, stopping and turning caused by shifting loads, thereby lessening driver burden and enabling more stable cargo transport. The feature is scheduled for implementation in additional Ruichi models going forward.
This development responds to conditions in China's urban areas, where e-commerce growth has fuelled demand for short-distance delivery services while autonomous driving and driver assistance features gain traction. In vehicles equipped with advanced systems, control logic typically operates based on predetermined load parameters. When actual loads deviate from these assumptions, discrepancies arise that affect driver comfort and cargo stability. Commercial vehicles therefore increasingly require smooth acceleration and deceleration control that remains effective regardless of load conditions.

Ruichi selected Dunlop's technology as an effective solution to these challenges. The system requires no additional sensors and can be installed without modifying existing vehicle configurations, offering significant cost advantages. SENSING CORE analyses wheel speed data alongside vehicle control information from the CAN data stream to detect various conditions including tyre pressure, tread wear and load.
On the Ruichi C5, the load detection function assesses total weight on left and right tyres for front and rear axles according to changes in cargo volume and position. This data optimises torque output during acceleration and brake control based on current load conditions, delivering stable ride quality unaffected by load changes during frequent urban deliveries.

Dunlop pursues this work under its SMART TYRE CONCEPT development philosophy, which aims to deliver high safety and environmental performance for CASE and MaaS applications. SENSING CORE anchors these services and is planned as the company's fourth major business pillar alongside tyres, sports and industrial products.
The challenges of frequent starts and stops during urban deliveries and changing load conditions extend beyond China throughout Asia, including Japan. Building on this adoption, Dunlop aims to expand its presence in both domestic and international markets.
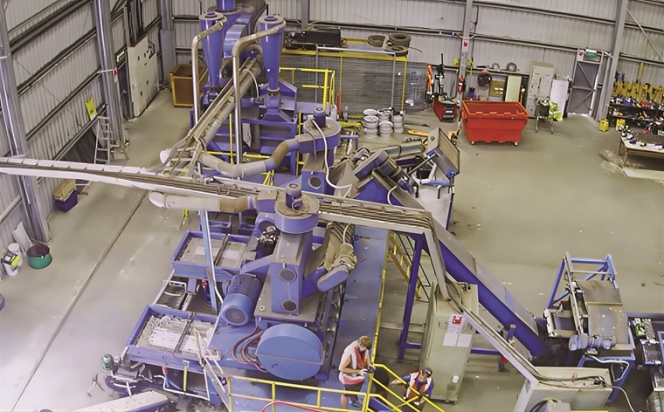

Refurbished tyre-recycling machines are emerging as a practical answer to rising compliance pressure and capital constraints across the sector. As demand grows for faster, lower-cost capacity expansion, Revyre Global’s decision to release a complete, operational processing line highlights how secondary equipment markets are becoming strategically relevant to recyclers.
Refurbished machines are finding renewed demand in the tyre-recycling industry as processors look to expand capacity quickly without the capital burden and long delivery cycles of new equipment.
Against this backdrop, New Zealand-based recycling firm Revyre Global is releasing a suite of previously used, fully operational machinery from its tyre-recycling line, offering other recyclers access to proven processing systems spanning shredding, separation and granulation, along with critical spares to support uninterrupted operations.

Speaking to Tyre Trends exclusively, Chief Executive Officer Shaun Zukor noted, “Demand for refurbished tyre‑recycling equipment is expected to increase as global EPR regulations intensify and scrutiny grows around whole‑bale tyre handling. Many operators are seeking leaner, downsized plant and equipment configurations to meet compliance requirements while reducing capital expenditure. As regulatory pressure mounts, refurbished systems present a practical and cost‑effective solution for meeting mandated recycling obligations.”
The equipment sale aligns with Revyre’s broader strategy to expand capacity and scale into new markets, particularly in roading and water-proofing applications where demand for high‑quality recycled polymer products is growing rapidly. These sectors require higher production volumes and upgrading to next‑generation technology positions the company to fulfil those larger‑scale opportunities.
The line for sale can produce approximately two tonnes per hour of product, which is standard with current smaller operational outputs. The new processing line’s output is highly adaptable and could be rapidly configured to produce a range of materials based on market demand.
“This flexible production capability allowed the system to switch between product types without significant downtime or reconfiguration, enabling throughput levels that aligned competitively with industry standards. The ability to modify production on demand ensured efficient utilisation of capacity under varying operational requirements,” explained Zukor.
The primary target buyers of the company are new market entrants with vertically integrated operations, particularly those managing tyre‑collection networks. Such buyers can benefit from processing tyres earlier in the value chain, improving transport efficiency by reducing bulk volume and lowering the need for extensive pre‑processing at the final facility. This machinery offers an accessible entry point for organisations seeking scalable, cost‑efficient recycling capability.
TURNING THE BLADES
According to Zukor, Revyre’s existing mechanical tyre‑shredding system faced significant operational constraints due to its reliance on multiple moving components, which resulted in frequent breakdowns, high maintenance costs and extensive downtime.
The traditional multi‑stage process viz-a-viz shredding, rasping and grinding required substantial manual supervision and labour input, creating both inefficiencies and higher operating expenditure. These limitations collectively hindered scalability and consistent production performance, prompting the shift to more advanced and efficient technology.
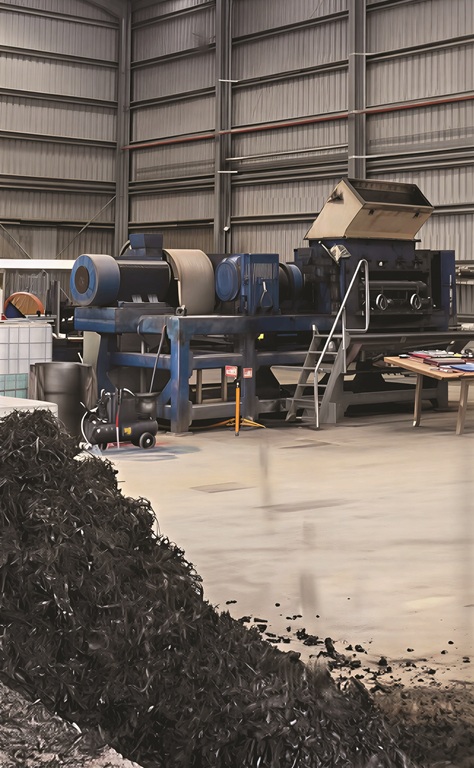 “The next‑generation system offers a markedly more automated process that consolidates material reduction into a single grinding stage. This significantly reduces maintenance requirements, labour dependency and risk of mechanical failure. The improved system delivers higher throughput rates, more consistent and higher‑purity output materials and substantially lower contamination levels. In addition, improved energy efficiency across the system contributes to lower operational costs and a more sustainable processing footprint,” explained Zukor.
“The next‑generation system offers a markedly more automated process that consolidates material reduction into a single grinding stage. This significantly reduces maintenance requirements, labour dependency and risk of mechanical failure. The improved system delivers higher throughput rates, more consistent and higher‑purity output materials and substantially lower contamination levels. In addition, improved energy efficiency across the system contributes to lower operational costs and a more sustainable processing footprint,” explained Zukor.
While all used equipment carries inherent operational risks, the system on sale recently underwent a repair and replacement of key wear components. “With proper upkeep, the line is expected to deliver at least another 10 years of reliable performance. The sale package includes spare parts and maintenance support to help buyers manage operational continuity and compliance requirements,” added Zukor.
He also noted that providing reliable, industrial‑grade equipment lowers capital barriers and reduces development time for new entrants. Furthermore, by extending the lifecycle of existing machinery, Revyre reinforces the principles of circularity, effectively recycling the recycling equipment, which is aligned with the organisation’s mission and sustainability values.
Currently, the company is actively advancing towards fully automated, digitally controlled recycling systems to reduce human exposure to mechanical processes and improve operational safety.
Increased automation will also reduce labour overheads and enables more consistent, globally competitive production output, supporting its long‑term vision of efficient, technology‑driven resource recovery.
“This upgrade is a major step towards establishing Revyre as a leader in high‑value polymer recovery, enabling production of superior‑grade materials for roading, water-proofing and masterbatch applications. Enhanced quality, scalability and process efficiency will strengthen our circular‑economy partnerships including potential collaborations with tyre manufacturers seeking reliable, high‑performance recycled inputs,” noted Zukor.
Revyre’s equipment sale underlines a broader shift in tyre recycling where affordability, compliance and speed to market matter as much as technology. By extending machinery lifecycles while upgrading its own capability, the company reflects an industry increasingly viewing refurbished systems as both an economic and circular solution.







Comments (0)
ADD COMMENT