Kokusai Drives Tyre Testing Into A New Era
- By Sharad Matade & Gaurav Nandi
- April 15, 2025

In an interview with Tyre Trends, Markus Winter, Director of Marketing and Sales at Kokusai Europe, and Kazuhiro Murauchi, Vice President and Head of Engineering at Kokusai Headquarter, share insightful perspectives on the fast-changing reality of tyre testing. With regulatory demands increasing and car technologies developing, Winter shares how the industry responds to new challenges presented by electric vehicles, tighter emission requirements and shifting consumer demands. With Kokusai manufacturing around 130 tyre test machines every year, Winter presents a special point of view regarding the technological advancements and market forces that are determining the future of tyre development and testing practices.
Every nook and cranny within tyre markets across the globe, big or small, is echoing a confluence of old and new practices in the age of new mobility. Attempts to constantly derive upcoming trends are massively influencing stakeholders within the tyre ecosystem as they mull over operational shifts for meeting future demands. The intricate world of tyre testing is also attuning itself to such changes to deliver a seamless transition to end users as progress unfolds.
Markus Winter, Director – Marketing and Sales, Kokusai Europe, contended that tyre testing has surged in recent times as emission norms become stricter and manufacturers methodically formulate new compounds to develop tyres for new-age vehicles.
“Over the past five to 10 years, tyre testing has undergone significant changes driven by regulatory pressures and evolving consumer expectations. In Europe, automotive manufacturers have prioritised high-speed uniformity testing to enhance ride comfort,” noted Winter while speaking exclusively to Tyre Trends.
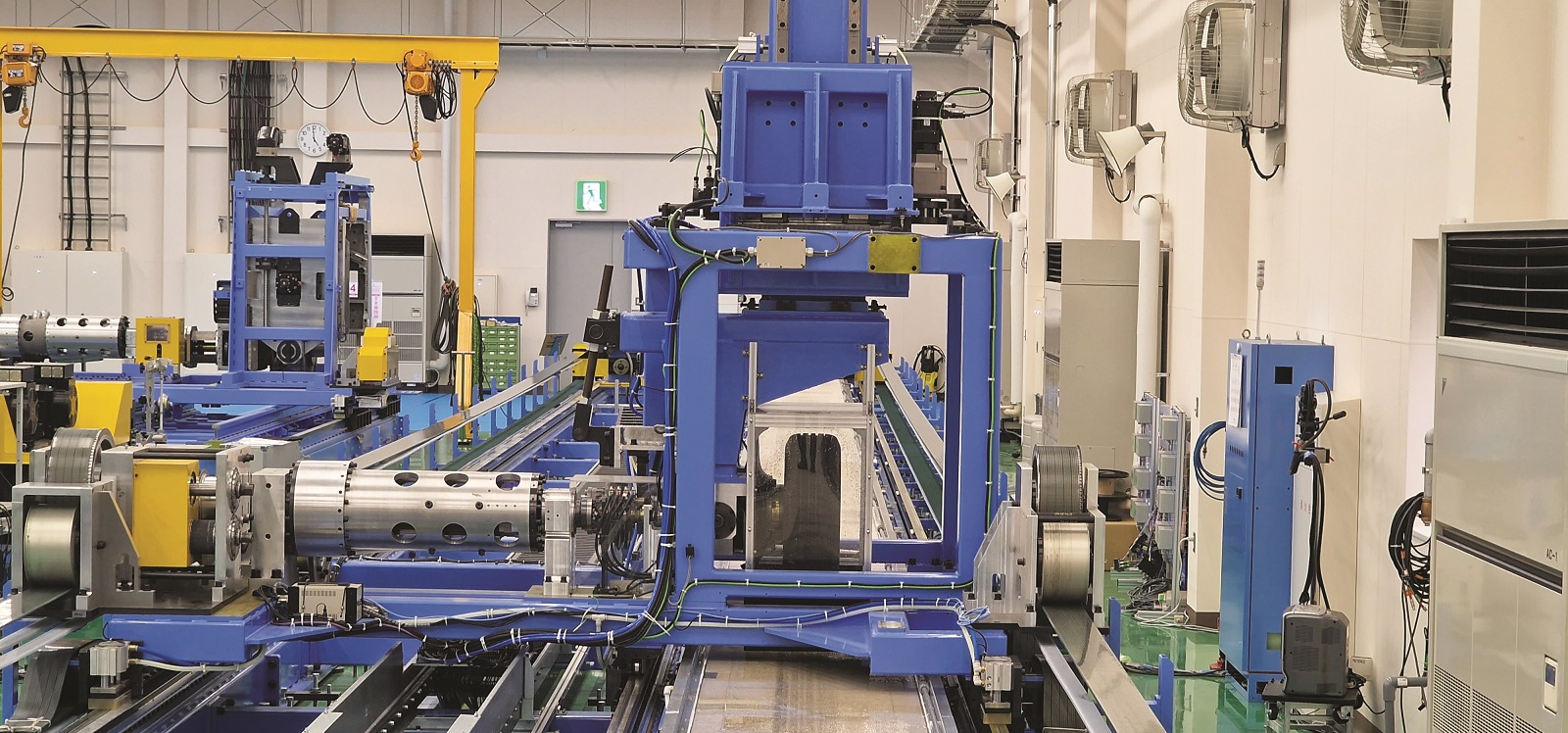 “Simultaneously, there has been a strong industry-wide push towards improving wet grip, not only for new tyres but also for worn ones. More recently, with the introduction of Euro 7 regulations, the spotlight has turned to wear testing. The emphasis is on minimising microplastic emissions and fine dust particles, aligning with broader environmental and health concerns. As regulatory scrutiny intensifies, tyre manufacturers are expected to invest further in wear-reduction technologies, shaping the next phase of innovation in the industry,” he said.
“Simultaneously, there has been a strong industry-wide push towards improving wet grip, not only for new tyres but also for worn ones. More recently, with the introduction of Euro 7 regulations, the spotlight has turned to wear testing. The emphasis is on minimising microplastic emissions and fine dust particles, aligning with broader environmental and health concerns. As regulatory scrutiny intensifies, tyre manufacturers are expected to invest further in wear-reduction technologies, shaping the next phase of innovation in the industry,” he said.
The Japan-headquartered company that produces around 130 tyre testing machines each year believes that Euro 7 regulations will impose stringent limits on wear particle emissions, leading to a major shake-up within the global tyre industry.
The new rules, targeting a 30 percent reduction in particulate emissions, could disqualify a substantial number of current tyre models from original equipment (OE) fitment on new vehicles. While exact figures remain uncertain, industry estimates suggest that up to 50 percent of existing tyre types may be phased out, with some projections even higher. This has placed immense pressure on manufacturers to accelerate testing and compliance efforts.
The initial response from tyre makers will likely focus on outdoor testing, given its simplicity. However, there is growing consensus that standardised drum testing will be essential for consistent evaluation. Over the next one to three years, demand for advanced wear testing solutions is expected to surge, creating significant business opportunities for testing providers.
At the same time, the industry is closely monitoring regulatory discussions and standardisation efforts as test methodologies continue to evolve. Regional differences are evident with Japanese and European manufacturers prioritising distinct approaches to compliance.
While no dedicated testing equipment for wear particle emissions exists yet, there is increasing interest in integrating sensors and analytical systems into existing tyre wear testing frameworks.
As regulations tighten, companies positioned at the forefront of wear testing innovation will be well-placed to capitalise on the shifting market dynamics.
SHIFTING DYNAMICS
The rise of electric vehicles (EVs) is fundamentally reshaping the tyre testing industry. With EVs requiring bigger, heavier tyres and delivering significantly higher torque, testing methodologies must adapt to these changing dynamics.
“With EVs demanding bigger, heavier tyres and generating higher torque, the industry must adapt. Our testing concepts are divided into two key areas including force and moment testing, which accounts for the torque and velocity changes and endurance testing such as tyre wear assessments. While high torque isn’t a requirement for endurance testing, these machines must still meet rigorous performance standards,” noted Winter.
Another major transformation is the accelerated development cycle of new tyres. Previously, a single tyre model would take six months to a year to develop, but manufacturers are now introducing new models every three months. Each iteration features different materials, tread designs and wear characteristics, increasing the need for highly flexible and efficient testing solutions. “This shift creates a greater demand for flexible, high-throughput testing solutions. We’ve opened a technical centre in Tokyo, where manufacturers can evaluate new tyre designs and test methods in real time,” informed Murauchi.
Smart tyre technology is also influencing the testing landscape. According to the executive, tyre testing involved manually recording data such as temperature, pressure and wear characteristics in the past. Today, with the integration of tyre pressure monitoring system sensors and RFID tracking, data collection is becoming increasingly automated. These advancements allow for real-time analysis and improved accuracy in performance evaluations. Although not all tyres currently include RFID technology, the trend is clearly moving towards fully automated data integration.
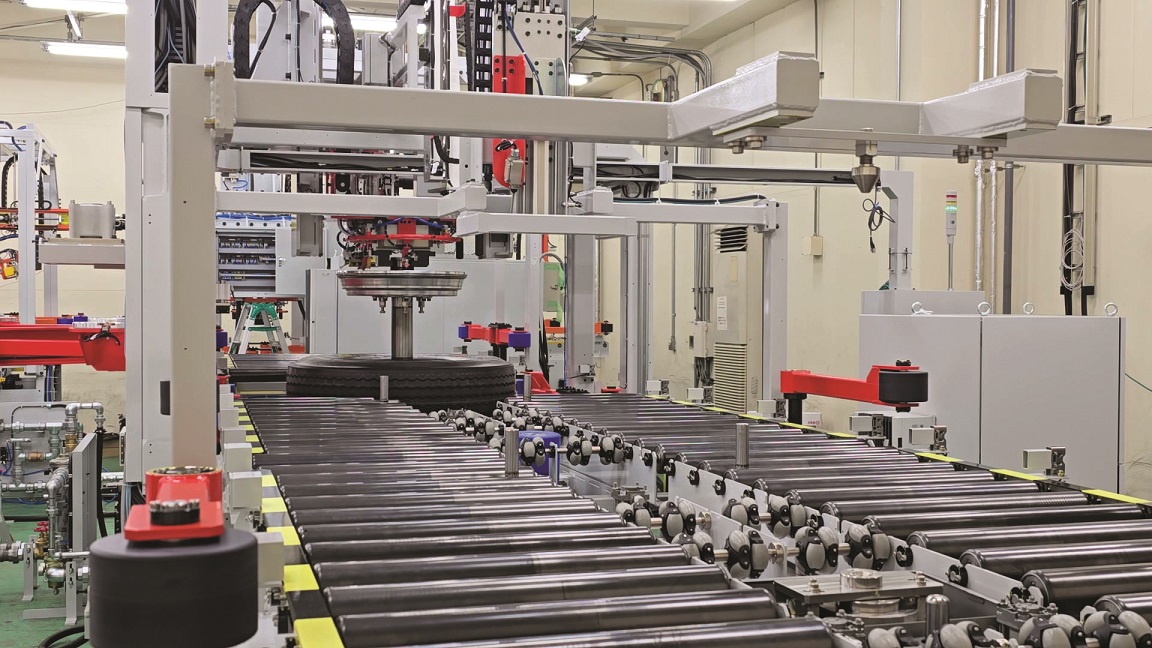

High-speed uniformity testing is another area undergoing transition. “Demand for this type of testing peaked several years ago, particularly for performance and luxury vehicles. However, as EVs continue to grow heavier, the impact of uniformity variations at high speeds has diminished. A vehicle that is 500–800 kg heavier places less emphasis on tyre uniformity, making it less of a critical factor for the driver. Despite this trend, high-speed uniformity testing remains essential in laboratory settings, where it provides valuable insights into braking performance, torque application and wet grip. While production-line high-speed testing has seen a slight decline, laboratory testing remains a necessary step in ensuring that EV tyres meet safety and performance standards,” noted Winter.
Investment trends in the industry also reflect this evolving landscape. Many tyre manufacturers are opting for outdoor testing because it requires lower upfront investment. Outdoor tests can be conducted by hiring test vehicles and drivers rather than investing in costly laboratory equipment.
Nonetheless, core testing parameters such as uniformity, geometry and balance will remain essential despite the shifts, noted the executive.
INTELLIGENT MACHINES
Winter noted that artificial intelligence (AI) will also play a significant role in tyre testing, particularly in analysing wear test results. While machine builders focus on developing equipment that ensures precise and reproducible testing conditions, AI is increasingly being used in areas like shearography testing.
“For now, AI’s role in direct test result analysis remains limited as interpreting the data largely falls to manufacturers. Testing machines must guarantee consistent results under identical conditions ensuring uniform abrasion rates. However, manufacturers leverage AI to assess tread compounds and wear conditions, an area beyond the machine builder’s core business,” said Murauchi.
Software is also becoming increasingly important in tyre testing, though integration varies by manufacturer size. Major companies prefer to use proprietary quality tools and focus on seamless data integration.
Smaller manufacturers, however, seek guidance on handling test data, creating opportunities for collaboration with software firms.
Despite handling vast amounts of test data, the company is not pursuing a business model centred on data analytics or test services. Some competitors have expanded into internal testing and data-driven solutions, but this firm remains committed to machine building.
UPGRADING SYSTEMS
Customers today are increasingly seeking testing machines that can be upgraded rather than replaced after 15–20 years. Their expectation is to minimise costs while extending the machine’s lifecycle, though upgrading a machine directly in a customer’s plant at minimal cost is not always feasible. Despite this, manufacturers are focusing on designing equipment that allows for easier upgrades over time.
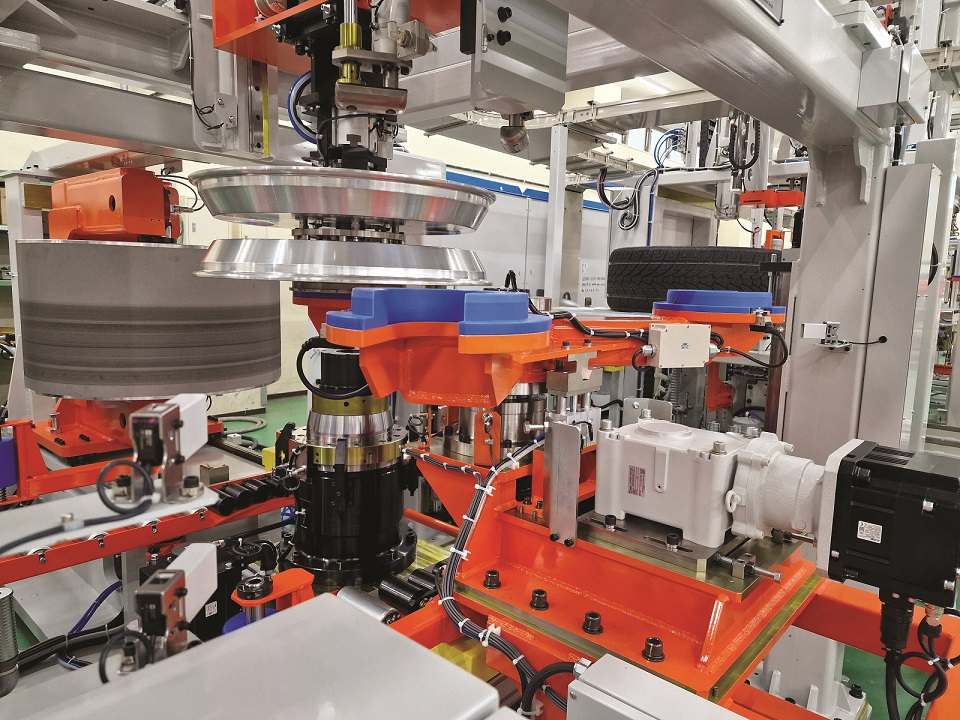 “One key aspect of this shift is the move away from hydraulic systems. All of our testing equipment is now fully electric, whether it is a compression tester, steering tester or vibration tester. This transition was influenced by Japan’s experience with earthquakes, particularly the 2011 disaster that led to power shortages. Following the Fukushima incident, the Japanese Government required manufacturers to reduce power consumption by 15 percent. Unlike hydraulic systems, which require stable oil temperature and pressure, our fully electric machines can be turned on and off instantly, making them more energy-efficient and reducing operational downtime,” averred Murauchi.
“One key aspect of this shift is the move away from hydraulic systems. All of our testing equipment is now fully electric, whether it is a compression tester, steering tester or vibration tester. This transition was influenced by Japan’s experience with earthquakes, particularly the 2011 disaster that led to power shortages. Following the Fukushima incident, the Japanese Government required manufacturers to reduce power consumption by 15 percent. Unlike hydraulic systems, which require stable oil temperature and pressure, our fully electric machines can be turned on and off instantly, making them more energy-efficient and reducing operational downtime,” averred Murauchi.
The focus on energy efficiency extends to long-term improvements in machine performance. Over the years, the company has developed systems that significantly reduce electricity consumption. Since tyre wear testers run for long durations daily, its energy usage directly impacts operating costs.
“We developed an innovative drive concept that provides force-synchronised control of the drum and test tyre, allowing tyre slip to be precisely applied via a highly dynamic torque-on-demand system. Combined with our specially adapted load case collective, this new system achieves a nearly 90 percent reduction in energy consumption compared to conventional hydraulically driven wear testers. As a result, we can dramatically reduce the running cost for our customers. The first sets of these advanced systems have already been successfully implemented at a major Japanese company, demonstrating the effectiveness of our energy-efficient approach,” revealed Winter.
REGULATORY CHANGES
Regulations play a critical role in shaping the tyre testing industry as manufacturers continuously adapt to new requirements. Winter anticipates significant regulatory changes, particularly in Europe and Asia, over the next four to five years that will impact tyre testing and development.
“One of the key upcoming regulations is related to tyre wear. There is increasing focus on how quickly tyres wear out and how that affects road safety and environmental impact. In addition to wear, the wet grip performance
of tyres is expected to come under stricter regulations, pushing manufacturers to provide more transparent data on its products’ real-world performance. Another area of growing interest is tyre lifespan, particularly for commercial truck and bus tyres. Customers are becoming more focused on the overall service life of tyres rather than just wear resistance, which means testing procedures may need to evolve,” said Winter.
“Tyre safety is another area where regulations are expected to tighten. In the past, tyre testing has primarily focused on new tyres, but we foresee that future regulations may require testing on worn tyres as well. This is because a new tyre performs optimally, but its behaviour can change significantly after use. Factors such as tread depth, air pressure variations and temperature fluctuations influence how a tyre performs over time, and regulators may demand better data on these aspects,” he added.
Currently, tyre testing is done under standard conditions, but in reality, tyres are used in extreme temperatures ranging from sub-zero to scorching heat. With the rise of autonomous driving, there is an increasing need for tyres to be tested in a variety of weather conditions.

Future regulations may require more comprehensive testing to ensure that tyres perform predictably across different temperatures, humidity levels and road conditions. Autonomous vehicle systems will likely rely on detailed tyre performance data to make real-time driving decisions, which could drive the development of new testing methodologies.
FOOTPRINT
Asia remains the strongest market for the company, where it has established itself as the market leader with deep customer relationships. While competition is intense in Europe, the company has tested its machines with premium manufacturers and is adapting its equipment to meet the specific needs of different tyre makers.
The company is deploying pilot projects across various segments including passenger car and truck tyres to expand in Europe. These initial installations allow for extended testing before securing approvals to participate in larger procurement processes. In contrast, the wear tester segment is less competitive with only a few global suppliers, positioning the company as a key player with extensive collaborations worldwide. The focus now is on strengthening technical partnerships, installing pilot units and integrating its solutions within the operational frameworks of major tyre makers.
The company has set a target to expand capacity to 150 units per year, potentially by the end of 2025. While European markets face margin pressures, the company’s challenge lies in scaling up production in Asia, US and Europe to meet growing global demand.
KraussMaffei Technologies Appoints Dirk Musser As New Managing Director
- By TT News
- February 27, 2026

KraussMaffei Group is set to implement a leadership transition at its subsidiary, KraussMaffei Technologies, with a change at the board level. Jörg Stech, who has served as Chairman of the Board and global head of injection moulding, automation and additive manufacturing since 2023, will be departing on 31 March 2026 at his own request. He will be succeeded by Dirk Musser, the current Head of Group Transformation at the parent company, who has been appointed as the new Managing Director effective 1 April 2026. The leadership handover between Stech and Musser is already in progress, ensuring a seamless transition.
Stech’s tenure unfolded during a difficult economic period marked by financial losses and a contracting market. He responded with decisive measures aimed at margin enhancement and balance sheet improvement, which laid the groundwork for the company's long-term stability. Under his direction, the product lineup for injection moulding and automation was revitalised with the introduction of the LRXplus linear robot, the fully electric PX series and the MC7 control system, all launched in late 2025 alongside new artificial intelligence tools. He also launched a multi-year development initiative and pushed the company into new markets, such as aerospace and drone technology, by leveraging expertise in specialised processes like ColorForm. Through a focus on operational excellence, pricing discipline and capital efficiency, Stech guided the company to a significantly more resilient position compared to three years prior, despite the persistent downturn in injection moulding.
Musser brings to his new role extensive experience in transformation and finance. In his current capacity, he has already been closely involved with KraussMaffei Technologies, collaborating with its leadership to drive strategic initiatives and enhance operational performance. His qualifications include sharp analytical abilities, a strong grasp of industrial processes and a broad international perspective. An economist by training, Musser has accumulated over 20 years of leadership experience across various technology and industrial sectors. His background includes leading major transformation and turnaround projects at CRRC New Material Technologies, where he stabilised plant earnings in North America, as well as directing operational and financial restructurings during his time at Deloitte. He has also held roles with P&L responsibility, managing global supply chains and post-merger integrations at CRONIMET and has prior experience with automotive manufacturers including Daimler and Fujian Benz Automotive in China.
Alex Li, CEO, KraussMaffei Group, said, "Jörg Stech took on responsibility in a difficult situation, set clear priorities and launched decisive initiatives. The successful market launch of the LRXplus linear robot and the all-electric PX machine series, the consistent focus on profitability and the sustainable strengthening of our balance sheet are visible results of this work. We would like to express our sincere thanks to Jörg Stech for his leadership, integrity and team spirit. We value Dirk Musser as a leader who combines strategic clarity with operational excellence. In a short period of time, he has provided vital impetus for the transformation of the group and impresses with his analytical strength, decisiveness and deep understanding of our processes – not least through his successful collaboration with the managing directors of KraussMaffei Technologies. We are convinced that he will continue on this path with clarity and creative drive to successfully align KraussMaffei Technologies."
Stech said, "After many years in an environment full of technological, economic and geopolitical challenges, I look back with great gratitude on a time in which I was always surrounded by an exceptional workforce. Together, we achieved things that many initially thought were impossible. This cooperation, this willingness to push boundaries and create something new, was a joy for me. My special thanks go to all stakeholders in the company and, of course, to all employees. I leave with respect, gratitude and the conviction that this long-established company will continue to achieve great things in the future."
Musser said, "Together with my fellow managing directors Dr Frank Szimmat and Markus Bauer, I want to resolutely drive forward the further development of KraussMaffei Technologies. Our focus is on further expanding stability and performance and taking the necessary steps to successfully position the company in a dynamic market environment. I look forward to shaping this path together with our teams.”
Dario Marrafuschi Succeeds Mario Isola As Pirelli’s Head Of Motorsport
- By TT News
- February 27, 2026

Italian tyre manufacturer Pirelli has announced that Dario Marrafuschi will become the Head of its Motorsport Business Unit, effective 1 March. He succeeds Mario Isola, who will remain with the company until 1 July to assist with the leadership transition.
Marrafuschi joined Pirelli in 2008 and has held positions within the Formula 1 Research and Development department. Most recently, he led the development of the company's road products.
He will report to Giovanni Tronchetti Provera, Executive Vice-President of Sustainability, New Mobility & Motorsport. The appointment comes as the company continues its role as the tyre supplier for various global motorsport categories.
Isola departs the company following a tenure that included the expansion of Pirelli’s motorsport operations. The company stated that Isola will pursue other professional opportunities following his departure in July.
Changing Tyre Dynamics In A Changing Car Market
- By Sharad Matade
- February 27, 2026
For Continental Tires India, the passenger vehicle market in India is entering a phase where scale and structure are finally aligning with its longstanding premium ambitions. Passenger vehicle sales reached a record 4.3 million units in 2024, expanding by 4–5 percent year on year, but it is the composition of that growth – rather than the headline volume – that is reshaping the company’s strategy. Utility vehicles now account for approximately 58 percent of total passenger vehicle sales, up sharply from about 51 percent the previous year, cementing SUVs and crossovers as the dominant force in the market.
This structural shift has direct consequences for tyre manufacturers operating at the upper end of the value spectrum. Larger vehicles bring higher kerb weights, bigger wheel diameters and greater expectations around refinement, safety and performance. For Continental, the change represents not merely an increase in addressable demand but a decisive move towards tyre categories where technology differentiation and pricing discipline can coexist.
Samir Gupta, Managing Director of Continental Tires India, calls this phase a turning point, not a temporary high. He says the surge in utility vehicles – driven by electrification and more premium cars – fundamentally changes the economics of the passenger tyre market in India.
“Let me clarify one thing first. The utility vehicle segment is no longer small. Last year, around 60 percent of passenger vehicles sold in India were utility vehicles, and including first-time buyers upgrading within this segment, the share goes beyond 65 percent,” Gupta says.

Industry data broadly supports this assessment. SUVs alone contributed close to three-fifths of all passenger vehicle sales in 2024, with compact utility vehicles accounting for a significant share of incremental volumes. The overall passenger vehicle market, at around 4.3 million units, has thus become structurally skewed towards larger formats – an inflection with long-term implications for tyre sizing, load ratings and product mix.
This shift shows in replacement demand. As vehicle footprints grow, rim diameters are increasing. “The market is clearly moving from smaller to bigger rim sizes. Demand for 17-inch and above tyres is rising sharply,” Gupta says. While these tyres are still a minority, their growth far outpaces the overall passenger tyre market.
Electrification is accelerating the shift. A substantial proportion of electric passenger vehicles sold in India today are SUVs, and Continental expects EVs to account for more than 50 percent of the passenger vehicle segment within five years. For tyre manufacturers, this creates new technical requirements – higher torque tolerance, lower rolling resistance and stringent noise control. “That creates a significant opportunity for us because our strengths lie in premium, high-performance tyres,” Gupta says.

Despite these favourable structural trends, premium tyres have historically struggled to gain traction in India. For much of the past decade, the market remained intensely price-sensitive, with tyres treated largely as commoditised replacement items. Continental’s response, Gupta explains, has been consistent rather than tactical pricing. “Right from the beginning, we have focused on fair pricing. The idea is simple – if we can clearly differentiate on performance and consistently deliver on those promises, price recovery will follow,” he explains.
The broader environment is now becoming more supportive. As vehicle prices rise and consumers migrate towards larger, more sophisticated vehicles, willingness to spend on tyres that enhance safety, comfort and driving confidence is increasing. This trend is also evident at the top end of the market. Premium and luxury passenger vehicle sales reached approximately 51,500 units in 2024, up around 6 percent year on year and crossing the 50,000-unit threshold for the first time – a symbolic marker of premium consumption in India.
Gupta sees premiumisation extending beyond luxury vehicles. “Earlier, India was extremely price-sensitive, but that is changing in higher segments. Consumers are upgrading vehicles and are more willing to invest in tyres that enhance safety, comfort and confidence,” he says.
The intensification of competition, with global premium tyre brands expanding or re-entering India, is viewed as a positive development. “Competition is always good,” Gupta says. “It gives you room to grow and improve.” More importantly, he believes it will help reframe the market. “More premium players will help move the market away from being purely cost-driven to being value-driven,” he adds.
Replacement market dynamics reinforce this view. Of the roughly 32–33 million passenger tyres replaced annually in India, tyres sized 17 inches and above account for about 12–13 percent. While the overall replacement market grows at 5–6 percent per year, this high-diameter segment is expanding at over 20 percent annually, closely tracking the shift in new vehicle sales.
This sharper focus on passenger tyres also explains Continental’s decision to exit the truck and bus radial segment in India. Gupta stresses that the decision was strategic rather than operational. Continental entered the TBR market in 2014, invested significantly and received strong feedback on product performance.
However, the economics proved limiting. Gupta says, “TBR in India is largely a B2B, fit-for-purpose market. Even if you have the best tyre, willingness to pay remains limited because fleet operators are under constant margin pressure.” Although commercial tyres offer higher absolute margins per unit, they consume substantially more raw material. “One commercial tyre uses six to eight times the raw material of a car tyre. Percentage margins are actually higher in passenger tyres,” Gupta explains.
After reviewing its portfolio, Continental chose focus over breadth. Exiting TBR allows the company to concentrate capital, technology and management attention on passenger and light truck tyres, where differentiation is more readily monetised. Gupta rejects the idea that a narrower portfolio weakens the company’s position. Commercial and passenger tyre customers, he argues, are fundamentally different – one driven by procurement economics, the other by consumer perception and emotion.
Indian consumers, Gupta believes, are becoming more tyre-aware. “Premiumisation is happening across the vehicle industry, not just in tyres. As consumers move to larger and more premium cars, their expectations also rise,” he says. Where tyres were once treated as an afterthought, buyers increasingly recognise their role in braking, grip, noise and overall driving confidence.
This change is evident at the retail level. Continental now operates more than 200 brand stores across India, and feedback from retail partners suggests customers are more informed and more demanding. Availability remains critical. “There is no point launching premium tyres if customers cannot find them,” Gupta says.
To support future demand, Continental is investing around INR 1 billion at its Modipuram plant, with the focus squarely on passenger and light truck tyres. The expansion will extend manufacturing capability from the current 20-inch limit to 22–23 inches, aligning local production with emerging vehicle trends.
Localisation, Gupta argues, is about adaptation rather than compromise. Indian road conditions, climate and driving habits require specific tuning without diluting global performance standards. Education and availability remain the principal challenges.
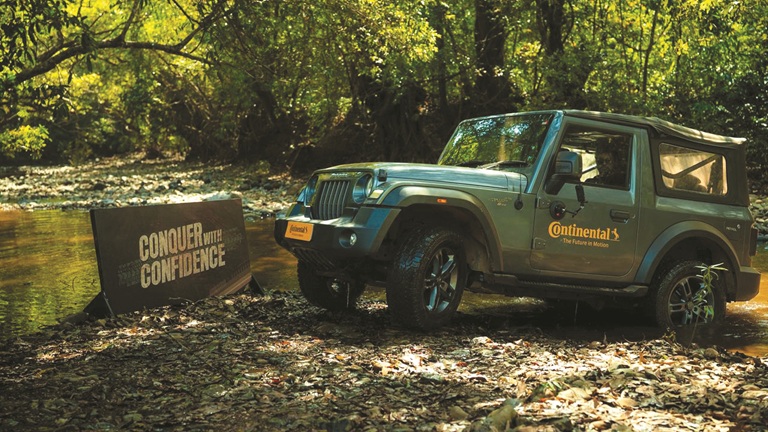

The recent launch of the CrossContact A/T² in India reflects this strategy. Introduced during Continental’s Track Day at Dot Goa 4x4, the product positions India among the early global markets for the tyre. “The first thing you notice is noise – or the lack of it,” Gupta says. “You hear the air-conditioning, not the tyre.” Ride comfort, grip and consistency across terrains define its appeal. As Gupta puts it, “Jahan tak soch jaati hai, wahan tak yeh tyre kaam karta hai.”
Looking ahead, Continental remains largely insulated from shifts in original equipment strategies, such as the gradual removal of spare tyres. Improved carcass design and stronger sidewalls are reducing puncture risk, but the company’s primary focus remains the replacement market.
For Gupta, the question is no longer whether India is ready for premium tyres, but how effectively manufacturers execute. “The market is finally ready for premium tyres,” he concludes. With passenger vehicle sales at record levels, SUVs firmly dominant and premium consumption expanding, Continental believes it is well positioned to grow alongside India’s evolving mobility landscape.
Falken Tyre Europe GmbH Rebrands As DUNLOP Tyre Europe GmbH
- By TT News
- February 26, 2026

Falken Tyre Europe GmbH has officially transitioned to operating under the name DUNLOP Tyre Europe GmbH, following its formal registration with the Offenbach Local Court. This change signifies a pivotal development for the Sumitomo Rubber Industries subsidiary. The rebranding represents a calculated and essential move to establish a more formidable European footprint for the DUNLOP brand. Company leadership acknowledges that this evolution is built upon the considerable equity established by Falken, including its strong market recognition, unwavering product quality and the commitment of its personnel.
This strategic shift positions the organisation under the umbrella of a globally respected marque, with its future strategy firmly centred on expansion, pioneering advancements and ecological responsibility. A prominent symbol of this new chapter will be unveiled shortly, with the renaming of the DUNLOP City Tower in Offenbach. A formal ceremony will mark the occasion, featuring the presentation of the DUNLOP logo at the tower. The event is set to be attended by Offenbach's Lord Mayor, Dr Felix Schwenke, alongside the company’s managing directors, Hiroshi Hamada and Markus Bögner, and the newly enlarged DUNLOP team.
Markus Bögner, Managing Director and President, DUNLOP Tyre Europe GmbH, said, “The name change is an important milestone of which we can be very proud. It strengthens our identity and underlines that we are ready for the next steps. Our strong heritage with Falken is and remains part of our success, laying the foundations for DUNLOP’s future in Europe. Our thanks go to all our employees and partners who have supported and accompanied us on this journey.”







Comments (0)
ADD COMMENT