Evonik Developing New Process To Make More Recycled Rubber Useable For New Tyres
- By TT News
- September 20, 2024

Evonik, one of the world leaders in speciality chemicals, is developing a new process that could make more recycled rubber useable for new tyres.
Because of its chemical structure, recycled rubber has been very limited in its suitability for use in new tyres. However, Evonik's research team has made significant progress with a new process that may allow for the use of up to four times as much recycled rubber in new tyres as previously possible. The development project by Evonik additionally bolsters the tyre manufacturers' extensive sustainability endeavours.
Normal production of new tyre rubber involves vulcanising raw rubber, sulphur and other ingredients. Applying pressure and heat causes the sulphur to link with the rubber's long carbon chains, creating a strong, three-dimensional network. That is also how tyre rubber from tyres nearing their end of life is structured. Nevertheless, the material's characteristics are different from non-vulcanised rubber because it has previously undergone vulcanisation. Currently, the top limit imposed by trade associations in the tyre recycling industry is an admixture of roughly five percent ground tyre rubber from end-of-life tyres. As a result, only a small proportion of recycled rubber powder is currently employed again in the production of new tyres. Furthermore, a lot of tyres nearing their end of life are still thermally reprocessed to be used as fuel for energy production. However, Evonik’s research team has now succeeded in reversing the vulcanisation of rubber to a large extent.
Christian Mani, Project Manager – Circularity, Evonik, said, “That brings us much closer to the key targets of sustainability and resource efficiency in this sector. Rubber is far too valuable a raw material to be used only once in tyres. We want to incorporate it into a circular system. By adding a special formulation containing vinyl silanes, the firm bonds in the recycled rubber can be split. We cleave the sulphur bridges in the rubber, yet leave as many of the long carbon chains as possible untouched.”
These vinyl silanes have already been successfully used for devulcanisation by the study team. In contrast to the above-mentioned technical criterion of about five percent, the percentage of recycle in the rubber blend could be increased to as much as 20 percent in testing. With test series and trials, Evonik is currently moving towards the next significant goals. Finding a solution that clients may use to industrial production in the near future is the goal. "Ultimately, our approach must prove convincing on a large, commercial scale,” added Mani.
- Dunlop
- Sumitomo Rubber Industries
- SENSING CORE Technology
- Tyre Load Detection
- Tyre Air Pressure Detection
- Ruichi
- Ruichi C5
SENSING CORE Technology Debuts In China’s Commercial EVs With Tyre Load Detection Feature
- By TT News
- March 04, 2026
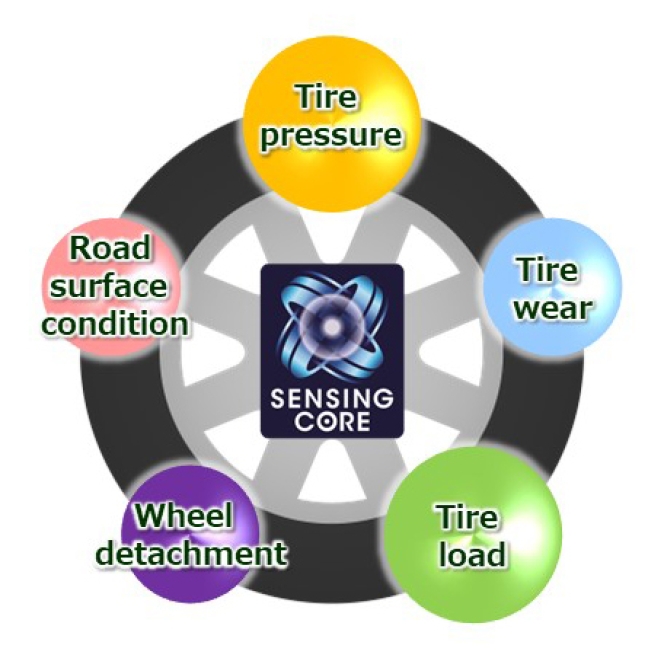
Dunlop (company name: Sumitomo Rubber Industries, Ltd.) has secured the first commercial deployment of its SENSING CORE technology in China. The system's ‘tyre load detection’ and ‘tyre air pressure detection’ functions have been adopted by Chongqing Ruichi Automotive Industry Co., Ltd. (Ruichi) for its new electric commercial vehicle model, the Ruichi C5. This marks both the technology's entry into the Chinese market and the global debut of Dunlop's tyre load detection capability.
The load detection function monitors changes in cargo weight and distribution in real time, feeding data to the vehicle's control system. This reduces driving instability during starting, stopping and turning caused by shifting loads, thereby lessening driver burden and enabling more stable cargo transport. The feature is scheduled for implementation in additional Ruichi models going forward.
This development responds to conditions in China's urban areas, where e-commerce growth has fuelled demand for short-distance delivery services while autonomous driving and driver assistance features gain traction. In vehicles equipped with advanced systems, control logic typically operates based on predetermined load parameters. When actual loads deviate from these assumptions, discrepancies arise that affect driver comfort and cargo stability. Commercial vehicles therefore increasingly require smooth acceleration and deceleration control that remains effective regardless of load conditions.

Ruichi selected Dunlop's technology as an effective solution to these challenges. The system requires no additional sensors and can be installed without modifying existing vehicle configurations, offering significant cost advantages. SENSING CORE analyses wheel speed data alongside vehicle control information from the CAN data stream to detect various conditions including tyre pressure, tread wear and load.
On the Ruichi C5, the load detection function assesses total weight on left and right tyres for front and rear axles according to changes in cargo volume and position. This data optimises torque output during acceleration and brake control based on current load conditions, delivering stable ride quality unaffected by load changes during frequent urban deliveries.

Dunlop pursues this work under its SMART TYRE CONCEPT development philosophy, which aims to deliver high safety and environmental performance for CASE and MaaS applications. SENSING CORE anchors these services and is planned as the company's fourth major business pillar alongside tyres, sports and industrial products.
The challenges of frequent starts and stops during urban deliveries and changing load conditions extend beyond China throughout Asia, including Japan. Building on this adoption, Dunlop aims to expand its presence in both domestic and international markets.
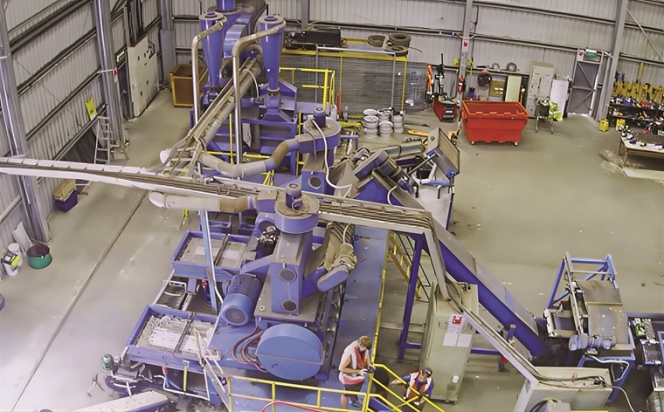

Refurbished tyre-recycling machines are emerging as a practical answer to rising compliance pressure and capital constraints across the sector. As demand grows for faster, lower-cost capacity expansion, Revyre Global’s decision to release a complete, operational processing line highlights how secondary equipment markets are becoming strategically relevant to recyclers.
Refurbished machines are finding renewed demand in the tyre-recycling industry as processors look to expand capacity quickly without the capital burden and long delivery cycles of new equipment.
Against this backdrop, New Zealand-based recycling firm Revyre Global is releasing a suite of previously used, fully operational machinery from its tyre-recycling line, offering other recyclers access to proven processing systems spanning shredding, separation and granulation, along with critical spares to support uninterrupted operations.

Speaking to Tyre Trends exclusively, Chief Executive Officer Shaun Zukor noted, “Demand for refurbished tyre‑recycling equipment is expected to increase as global EPR regulations intensify and scrutiny grows around whole‑bale tyre handling. Many operators are seeking leaner, downsized plant and equipment configurations to meet compliance requirements while reducing capital expenditure. As regulatory pressure mounts, refurbished systems present a practical and cost‑effective solution for meeting mandated recycling obligations.”
The equipment sale aligns with Revyre’s broader strategy to expand capacity and scale into new markets, particularly in roading and water-proofing applications where demand for high‑quality recycled polymer products is growing rapidly. These sectors require higher production volumes and upgrading to next‑generation technology positions the company to fulfil those larger‑scale opportunities.
The line for sale can produce approximately two tonnes per hour of product, which is standard with current smaller operational outputs. The new processing line’s output is highly adaptable and could be rapidly configured to produce a range of materials based on market demand.
“This flexible production capability allowed the system to switch between product types without significant downtime or reconfiguration, enabling throughput levels that aligned competitively with industry standards. The ability to modify production on demand ensured efficient utilisation of capacity under varying operational requirements,” explained Zukor.
The primary target buyers of the company are new market entrants with vertically integrated operations, particularly those managing tyre‑collection networks. Such buyers can benefit from processing tyres earlier in the value chain, improving transport efficiency by reducing bulk volume and lowering the need for extensive pre‑processing at the final facility. This machinery offers an accessible entry point for organisations seeking scalable, cost‑efficient recycling capability.
TURNING THE BLADES
According to Zukor, Revyre’s existing mechanical tyre‑shredding system faced significant operational constraints due to its reliance on multiple moving components, which resulted in frequent breakdowns, high maintenance costs and extensive downtime.
The traditional multi‑stage process viz-a-viz shredding, rasping and grinding required substantial manual supervision and labour input, creating both inefficiencies and higher operating expenditure. These limitations collectively hindered scalability and consistent production performance, prompting the shift to more advanced and efficient technology.
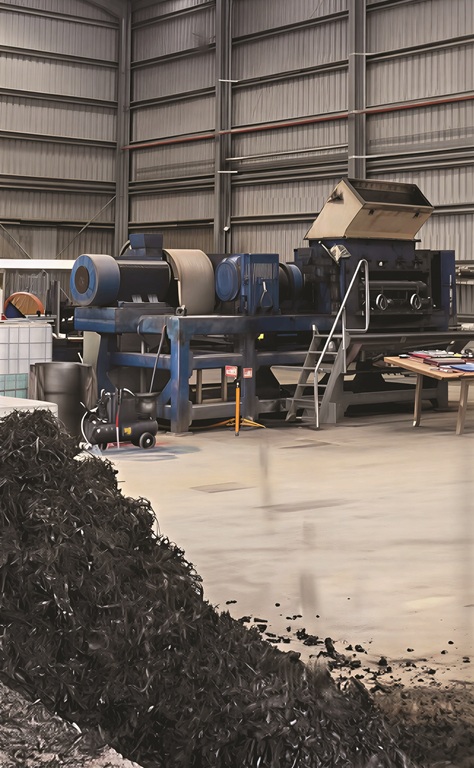 “The next‑generation system offers a markedly more automated process that consolidates material reduction into a single grinding stage. This significantly reduces maintenance requirements, labour dependency and risk of mechanical failure. The improved system delivers higher throughput rates, more consistent and higher‑purity output materials and substantially lower contamination levels. In addition, improved energy efficiency across the system contributes to lower operational costs and a more sustainable processing footprint,” explained Zukor.
“The next‑generation system offers a markedly more automated process that consolidates material reduction into a single grinding stage. This significantly reduces maintenance requirements, labour dependency and risk of mechanical failure. The improved system delivers higher throughput rates, more consistent and higher‑purity output materials and substantially lower contamination levels. In addition, improved energy efficiency across the system contributes to lower operational costs and a more sustainable processing footprint,” explained Zukor.
While all used equipment carries inherent operational risks, the system on sale recently underwent a repair and replacement of key wear components. “With proper upkeep, the line is expected to deliver at least another 10 years of reliable performance. The sale package includes spare parts and maintenance support to help buyers manage operational continuity and compliance requirements,” added Zukor.
He also noted that providing reliable, industrial‑grade equipment lowers capital barriers and reduces development time for new entrants. Furthermore, by extending the lifecycle of existing machinery, Revyre reinforces the principles of circularity, effectively recycling the recycling equipment, which is aligned with the organisation’s mission and sustainability values.
Currently, the company is actively advancing towards fully automated, digitally controlled recycling systems to reduce human exposure to mechanical processes and improve operational safety.
Increased automation will also reduce labour overheads and enables more consistent, globally competitive production output, supporting its long‑term vision of efficient, technology‑driven resource recovery.
“This upgrade is a major step towards establishing Revyre as a leader in high‑value polymer recovery, enabling production of superior‑grade materials for roading, water-proofing and masterbatch applications. Enhanced quality, scalability and process efficiency will strengthen our circular‑economy partnerships including potential collaborations with tyre manufacturers seeking reliable, high‑performance recycled inputs,” noted Zukor.
Revyre’s equipment sale underlines a broader shift in tyre recycling where affordability, compliance and speed to market matter as much as technology. By extending machinery lifecycles while upgrading its own capability, the company reflects an industry increasingly viewing refurbished systems as both an economic and circular solution.
Bridgestone’s Driver-in-the-Loop Simulator Goes Live
- By TT News
- February 25, 2026

Bridgestone has marked a significant advancement in its pursuit of digital mobility solutions with the activation of a cutting-edge driving simulator at its European R&D facility near Rome. The VI-grade DiM500 Driver-in-the-Loop (DiL) simulator represents a major step forward in the company’s virtual tyre development capabilities, allowing for the evaluation of tyre performance without the need for physical track testing.
The simulator is built around a large, mobile platform capable of moving up to five metres, enabling it to replicate the dynamic forces experienced in real-world driving. Housed within a carbon-fibre cockpit, the driver is immersed in a hyper-realistic virtual environment, and the system’s extensive range of motion ensures that the forces simulated are comparable to those measured during physical trials. This setup allows for highly accurate assessments of tyre behaviour.

By combining high-fidelity simulation with live driver feedback, historical data and artificial intelligence, Bridgestone can now explore a much wider array of tyre specifications earlier in the design phase. This approach accelerates design decisions and reduces the reliance on physical prototyping. Consequently, traditional track testing can be reserved for the final validation stages. This shift is expected to deliver substantial environmental benefits, with a projected annual saving of up to 12,000 experimental tyres. It builds on the company’s existing Virtual Tyre Development technology, which has already reduced raw material use and CO2 emissions in the original equipment development phase by as much as 60 percent.

Beyond environmental gains, the technology shortens development timelines by enabling simultaneous tyre and vehicle engineering. This parallel process fosters closer collaboration with automotive manufacturers, allowing Bridgestone to tailor tyres more precisely to the performance characteristics of specific vehicle models. While the simulator is currently focused on dry handling scenarios, its capabilities are being extended to cover a broader spectrum of driving conditions. Supported by continued investment in global research and development, this initiative reinforces Bridgestone’s capacity to adapt to the evolving demands of both manufacturers and drivers.

Mattia Giustiniano, Senior Vice President – R&D, Bridgestone West, said, “Bridgestone is already considered a pioneer in digital tyre development – leveraging Virtual Tyre Development for more than a decade. By integrating the driver into the digital development cycle, this investment adds a crucial new piece to our evolving ecosystem. The simulator’s introduction marks a significant step in enhancing the efficiency and sustainability of our R&D processes while unlocking unprecedented opportunities to foster innovation.”
Innovations Theater To Highlight VMI's Presence At Tire Technology Expo 2026
- By TT News
- February 25, 2026

VMI will showcase its latest tyre manufacturing technologies at Tire Technology Expo 2026, scheduled for 3–5 March 2026 in Hannover, Germany. The company will operate from booth 8064 in Hall 21, featuring the return of its Innovations Theater for a second consecutive year.
Specialists from VMI will deliver a series of 15-minute presentations at the theatre, covering recent product developments and technological advancements. Topics include the AMC on MAXX system, new features for the VMI MILEXX and the Batch Off Closed Air Circulation technology. Representatives from the VMI Services team will also discuss offerings such as VPC, VMS+, remote guidance, training programmes and retrofits. No advance registration is required for these sessions.
For conference attendees, Marzieh Salehi will present on the laboratory perspective for tyre and road wear particle (TRWP) collection and detection. The presentation is scheduled for Wednesday, 4 March, at 16:10 in the Five Continents conference room.
VMI, a company with a longstanding focus on tyre industry innovation, develops advanced machinery and services aimed at supporting customer operations and shaping the future of tyre production. Its participation in the expo reflects a commitment to providing cutting-edge solutions designed to meet industry challenges and drive progress in tyre manufacturing.







Comments (0)
ADD COMMENT