
Michelin’s CO2 emissions-reduction targets have been validated by SBTi, a leading independent collaborative organisation in this field.
The success of the COP21 Paris Climate Agreement depends not only on the commitment of member States but also on the involvement of civil society and the private sector in collectively reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
That’s why Michelin Group voluntarily submitted its CO2 emissions reduction targets to the SBTi for approval.
Michelin commits to reduce absolute scope 1 and 2 GHG emissions by +38% by 2030 from a 2010 base year. Michelin commits to reduce absolute scope 3 GHG emissions from fuel- and energy-related activities; upstream and downstream transportation and distribution; and end-of-life treatment of sold products by +15% by 2030 from a 2018 base year. Michelin also commits that +70% of its suppliers by emissions covering purchased goods and services will have science-based targets by 2024.
Scope 1 emissions are generated by sources owned or controlled by the Company, while Scope 2 emissions result from the generation of energy that is purchased and consumed by the Company. Scope 3 covers emissions resulting from the company's business but generated by sources not owned or controlled by the Company.
Obtaining approval from SBTi represents a first step toward carbon neutrality by paving the way for net-zero Scope 1 and 2 emissions at all Michelin sites by 2050.
The SBTi method is also an opportunity for Michelin to strengthen its commitment to its suppliers, in order to increase their societal responsibility through targeted action on CO2 emissions reduction in the production of raw materials.
“Gaining SBTi’s approval of our CO2 reduction targets is additional proof of the pertinence of our environmental strategy. Michelin Group has great ambitions, fully in line with its strategy, and a very long-term vision with regard to the fight against global warming. I firmly believe that for all of our business lines, the current crisis is an opportunity to step up our activities, products and initiatives aimed at protecting the environment,” said Florent Menegaux, Michelin Group CEO
Global Natural Rubber Market Tightens Amid Improved Demand, ANRPC Reports
- By TT News
- November 07, 2025
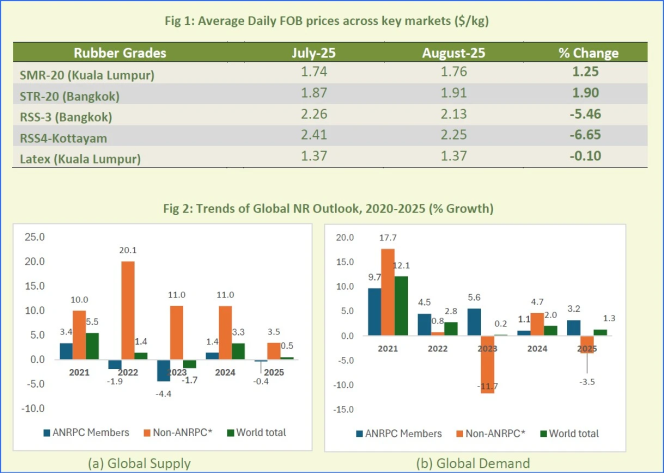
The global natural rubber (NR) market experienced fluctuating prices in August 2025 as supply constraints coincided with signs of improving demand, the Association of Natural Rubber Producing Countries (ANRPC) said in its latest Monthly NR Statistical Report.
The association noted that seasonal factors supported stronger consumption, particularly in China, where declining port inventories signalled healthier demand. However, heavy rainfall and labour shortages in key producing regions curtailed tapping activities, tightening supply conditions.
“Natural rubber prices experienced a fluctuating trend due to several factors, including constrained supply and improving demand,” ANRPC said. “Seasonal factors boosted consumption, particularly in China, where inventory reductions at major ports indicated improved demand. However, rainfall and labour shortages in producing regions limited tapping activities, tightening supply.”
According to updated data from member countries, global natural rubber production is projected to increase by 0.5 percent in 2025 compared with 2024, while demand is expected to grow by 1.3 percent over the same period.
The association said market sentiment had turned “increasingly optimistic” with stronger purchasing interest, driven by the traditional peak season for natural rubber, especially from the all-steel tyre and heavy-duty truck segments.
The ANRPC encouraged subscribers and stakeholders seeking more in-depth insights to refer to the full report or contact the ANRPC Secretariat for subscription details.
India Opens Anti-dumping Probe Into Halobutyl Rubber Imports From China, Singapore And US
- By Sharad Matade
- November 06, 2025

India has launched an anti-dumping investigation into imports of Halo-Isobutene-Isoprene Rubber (HIIR) from China, Singapore and the United States, following a complaint from Reliance Sibur Elastomers Private Limited, the Directorate General of Trade Remedies (DGTR) said in a notification.
The domestic producer alleged that the three countries were exporting the rubber to India at unfairly low prices, causing injury to the local industry. The company has sought the imposition of anti-dumping duties on the product, which is used in tyre inner liners, hoses, seals, tank linings, conveyor belts and protective clothing.
The DGTR said there was prima facie evidence that imports had risen “significantly” and were being sold below normal value, resulting in price depression and affecting the domestic manufacturer’s capacity utilisation and profitability. The authority noted that the dumping “is causing material injury to the domestic industry”.
The investigation will cover the period from July 2024 to June 2025, with an examination of injury trends dating back to April 2021.
HIIR, also known as halobutyl rubber, is classified under the broader synthetic rubber tariff category. Reliance Sibur Elastomers is currently the only producer of the material within India.
If the investigation confirms dumping and injury, the DGTR may recommend the imposition of duties to offset the impact and “remove the injury to the domestic industry”. Interested parties have 30 days to submit data and make their representations to the authority.
Global Carbon Black Market To Hit USD 44.8 Bln By 2034, Driven By Tyre And Autom Demand
- By TT News
- November 06, 2025
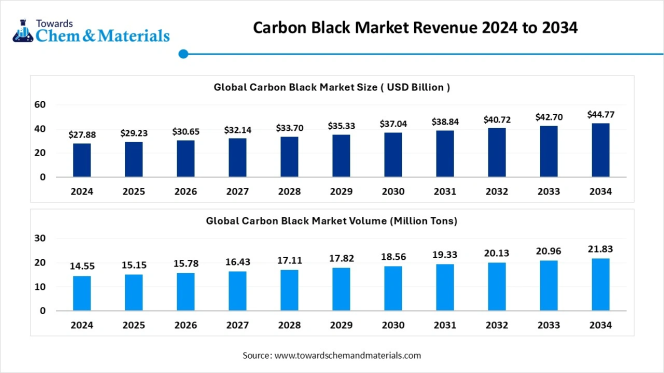
The global carbon black market is projected to grow from USD 27.88 billion in 2024 to USD 44.77 billion by 2034, expanding at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.85 percent between 2025 and 2034, according to a new report by Towards Chemical and Materials, a research arm of Precedence Research.
The study estimates that the global market volume will rise from around 15.15 million tonnes in 2025 to 21.83 million tonnes by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 4.14 percent, driven primarily by increasing demand for tyres, automotive components and high-performance plastics.
Carbon black – a fine black powder made through the incomplete combustion of hydrocarbons – is a critical material used to reinforce rubber in tyre production and enhance strength, durability and UV resistance in plastics, coatings, and batteries.
Asia Pacific accounted for about 58 percent of global market share in 2024 and is expected to remain the largest and fastest-growing regional market, supported by expanding tyre and rubber manufacturing bases in China, India and Southeast Asia. The region’s carbon black market was valued at USD 16.95 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 26 billion by 2034.
“The Asia Pacific region continues to lead both in production and consumption of carbon black, owing to its strong automotive, tyre and plastics industries,” the report noted, adding that China remains the world’s largest producer and consumer.
The furnace black segment dominated the market in 2024, accounting for about 60 percent of global industry share, due to its superior reinforcing properties in tyres and versatility in plastics and coatings. Meanwhile, the tyres and rubber products segment held a 55 percent share, reflecting the material’s indispensable role in the automotive sector.
Performance applications such as batteries, conductive polymers, and specialty coatings are emerging as key growth drivers. Demand for specialty carbon black and conductive grades is rising with the proliferation of electric vehicles, renewable energy systems, and electronics manufacturing.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is also shaping the carbon black industry, with automation and predictive analytics enhancing process efficiency, product consistency, and sustainability, the report said. AI-driven systems are enabling real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance in production plants, reducing waste and energy consumption.
Sustainability remains a key trend, with manufacturers investing in greener technologies, renewable feedstocks and recovered carbon black (rCB) from recycled tyres to meet circular economy goals. “Turning end-of-life tyres and rubber waste into recycled carbon black is opening new sustainable pathways for producers,” the study noted.
Among key players profiled in the report are Tokai Carbon Co., Ltd., Continental Carbon, Jiangsu C-Chem Co., Ltd., Himadri Speciality Chemical Ltd., Sid Richardson Carbon & Energy Company, Cancarb Limited, Philips Carbon Black Ltd., OCI Company Ltd., Columbian Chemicals Co. (Birla Carbon), Aditya Birla Group, and Raven SR, LLC.
Recent industry developments include PCBL Chemical Ltd.’s establishment of a wholly owned US subsidiary in Delaware in July 2025 to enhance supply chain localisation and strengthen its North American footprint, as well as the West Bengal government’s efforts to attract foreign investment in its carbon black industry to support the electric vehicle, tyre, and battery markets.
The report also forecasts rapid growth in North America, fuelled by clean manufacturing practices, sustainable process adoption and expansion in high-performance plastics and battery applications. Europe, meanwhile, is benefiting from stricter environmental regulations and the EU Green Deal, which are promoting eco-friendly and specialty grades.
The global carbon black market is expected to maintain steady long-term growth as manufacturers diversify into advanced applications and invest in sustainable production technologies to meet evolving industrial and environmental demands.
Kraton To Streamline Berre Polymer Operations Focus
- By TT News
- October 26, 2025

Kraton Corporation, a leading global producer of speciality polymers and high-value biobased products derived from pine chemicals, has revealed a new strategic initiative for its Berre, France facility. The plan involves streamlining its polymer operations to concentrate exclusively on manufacturing USBC products, which will result in the cessation of HSBC production at that site.
This move is designed to bolster Kraton's long-term competitiveness by optimising its manufacturing footprint in reaction to a global overcapacity for HSBC. The company has formally started an information and consultation process with the local Works Councils, with a final decision expected following this mandatory period. The company has reaffirmed its commitment to supplying HSBC from its broader global network and to leveraging its worldwide presence to continue adapting to market demands.
Prakash Kolluri, President, Kraton Polymers, said, “Our aim with this plan is to strengthen Kraton’s long-term competitive position by optimising our manufacturing footprint in response to changing market dynamics associated with global overcapacity of HSBC production capability. With this step, we are preparing Kraton for a sustainable future by securing Kraton’s position as the leading global HSBC producer. Kraton is fully committed to supporting our customers through this transition with supply of HSBC products produced within our unmatched global manufacturing network. We recognise the impact of these actions, and are committed to a safe, respectful and supportive transition. The health, safety and well-being of the employees remain our top priorities.”







Comments (0)
ADD COMMENT